Svelte从入门到精通——变量更新
发表于 阅读时长14分钟
目录
解析表达式
目前,我们在标签内的展示内容,都是静态文本。这一章,我们添加对诸如<div>{count}</div>形式内容的支持。
首先在parseFragment方法中添加parseExpression方法:
function parseFragment() {
return parseScript() ?? parseElement() ?? parseText() ?? parseExpression();
}
function parseExpression() {
if (match('{')) {
eat('{');
const expression = parseJavaScript();
eat('}');
return {
type: 'Expression',
expression,
};
}
}
在《解析html》章节,我们已经实现了parseJavaScript的支持,其功能就是调用acorn的parseExpressionAt方法。parseExpression返回type: 'Expression'类型的对象。
完善generate内的traverse方法:
function traverse(node, parent) {
switch(node.type) {
...
case 'Expression': {
const variableName = `exp_${counter++}`;
const expressionStr = escodegen.generate(node.expression);
code.variables.push(variableName);
code.create.push(
`${variableName} = text(${expressionStr})`
);
code.create.push(`append(${parent}, ${variableName});`);
break;
}
}
}
对于Expression类型的对象,调用escodegen.generate来生成js代码。
修改App.svelte的内容,同时我们把原来的button自定义样式移除。
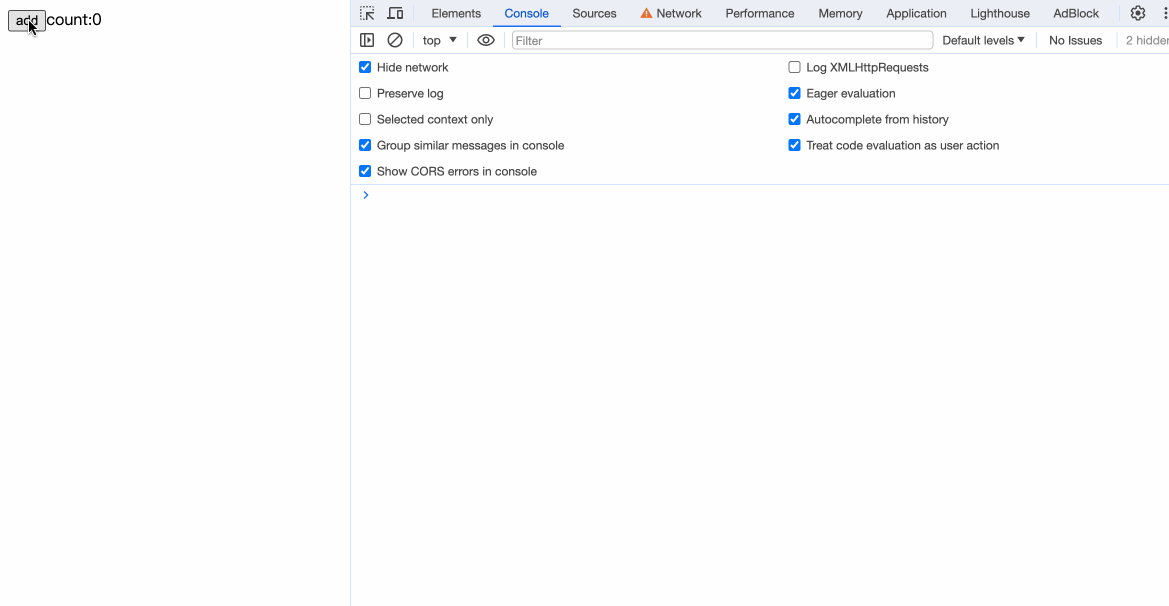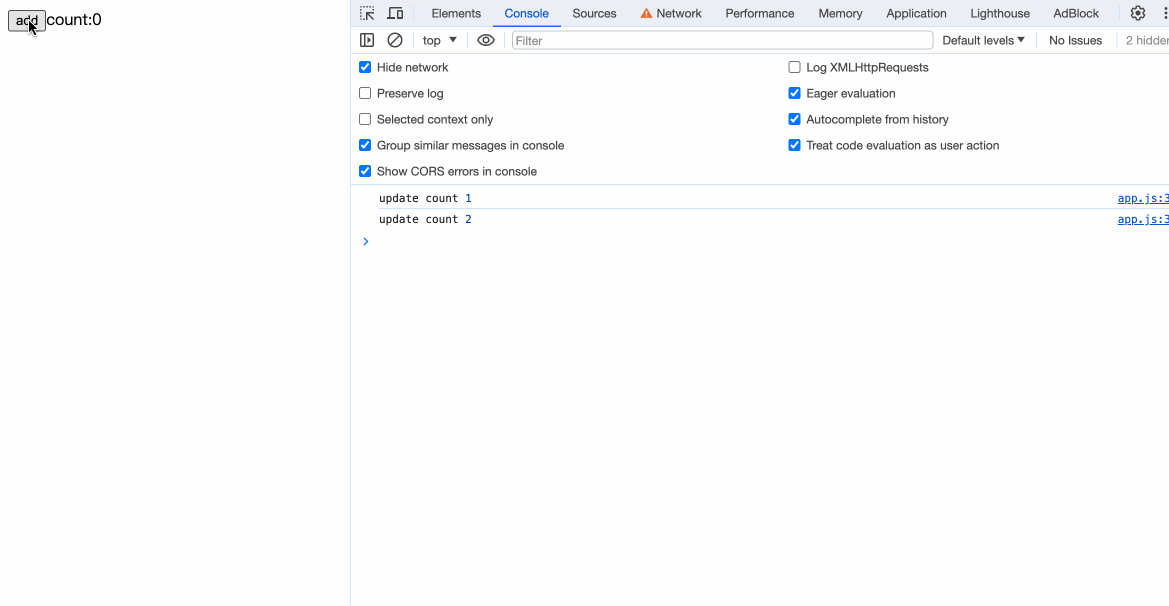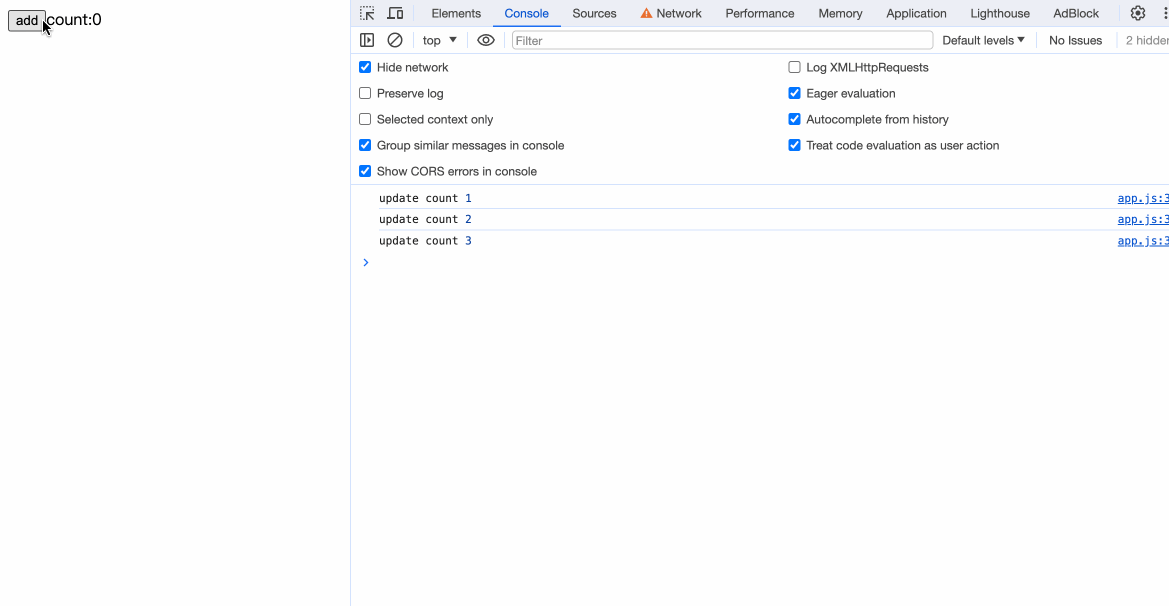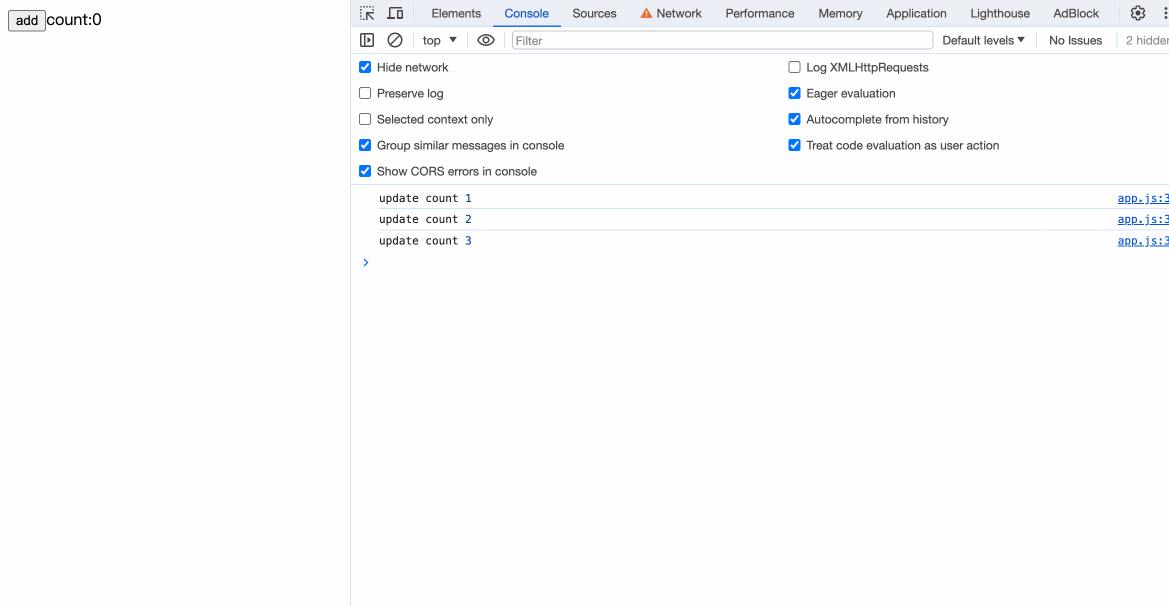
通过编译后的方法中,我们可以看到:
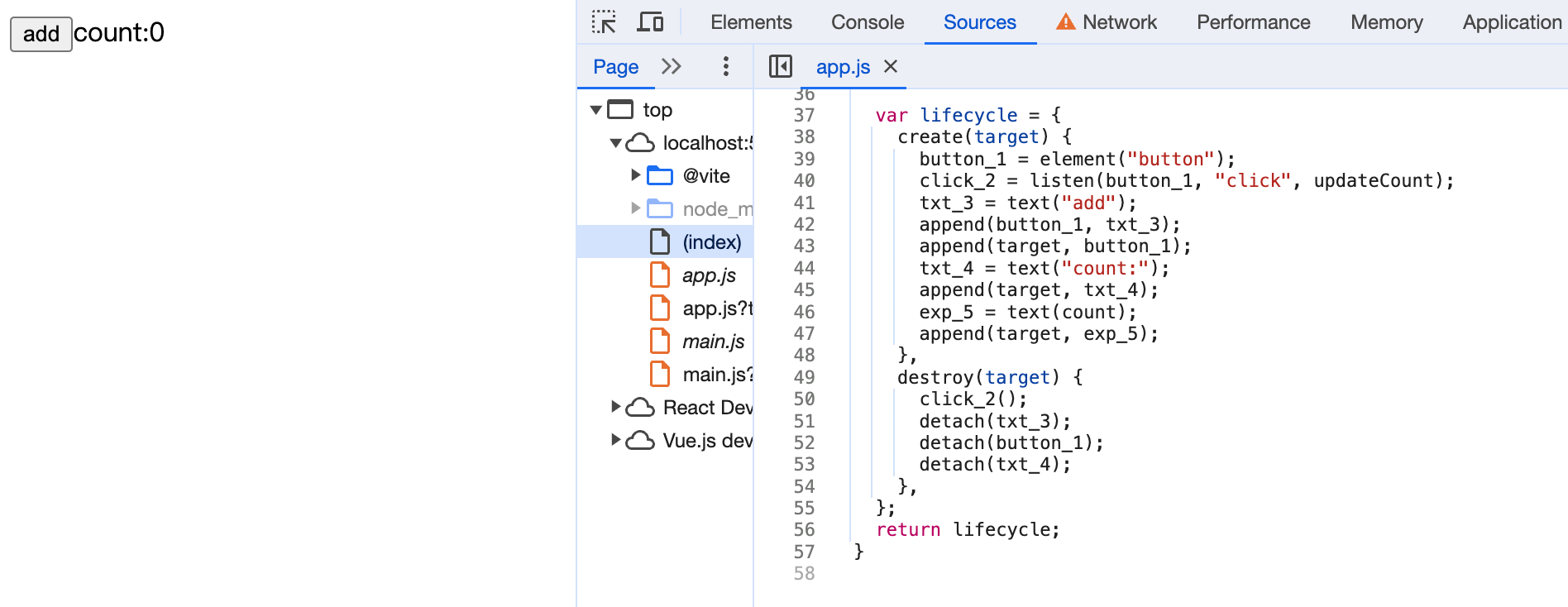
我们的{count}已经能被编译成exp_5 = text(count)。现在我们还差关键的一步:更新状态。
静态分析
我们知道Svelte是在静态代码阶段就解析出变量之间的关系,从而实现了响应式。首先我们定义一个analyse方法,用来解析代码中变量之间的关系,然后在生成阶段,我们会用到这部分数据。
function compile(content) {
const ast = parse(content); // 解析svelte文件内容成ast
const analysis = analyse(ast);
return generate(ast, analysis);
}
function analyse(ast) {
const result = {
variables: new Set(),
willChange: new Set(),
useInTemplate: new Set(),
};
return result;
}
result对象中有三个属性:viriables记录声明的变量,willChange记录会触发更新的变量,useInTemplate记录在html模板内容中使用到的变量。使用Set集合来确保我们记录到的变量唯一不重复。
解析script
安装estree-walker和periscopic。estree-walker用来编译ast对象,periscopic用来分析代码的作用域。
npm install estree-walker periscopic -D
import * as fs from "fs";
import { fileURLToPath } from "url";
import { dirname, resolve } from "path";
import * as acorn from "acorn";
import * as escodegen from "escodegen";
import * as prettier from "prettier";
+ import * as estreewalker from "estree-walker";
+ import * as periscopic from "periscopic";
function analyse(ast) {
...
const { scope: rootScope, map, globals } = periscopic.analyze(ast.script);
result.variables = new Set(rootScope.declarations.keys());
result.rootScope = rootScope;
result.map = map;
let currentScope = rootScope;
estreewalker.walk(ast.script, {
enter(node) {
if (map.has(node)) {
currentScope = map.get(node)
}
if (node.type === 'UpdateExpression' || node.type === 'AssignmentExpression') {
const names = periscopic.extract_names(node.type === 'UpdateExpression' ? node.argument : node.left);
for(const name of names) {
if (currentScope.find_owner(name) === rootScope || globals.has(name)) {
result.willChange.add(name);
}
}
}
},
leave(node) {
if (map.has(node)) {
currentScope = currentScope.parent;
}
}
})
}
- 首先我们用
periscopic来analysescript标签内代码的作用域,rootScope.declarations.keys()能够拿到我们定义在script标签内声明的所有变量。 - 使用
estreewalker来遍历script的抽象语法树。enter方法首先拿到当前节点的作用域。然后如果节点的类型是UpdateExpression或AssignmentExpression,它将提取出所有的变量名,并检查这些名字是否在根作用域(rootScope)或全局变量(globals)中。如果是,将这些名字加入到willChange变量中。 - 离开节点时重置作用域
我们举个简单的例子来演示下:
import * as acorn from 'acorn';
import { extract_names } from 'periscopic';
import { walk } from "estree-walker";
export let a = `let a = 0;
let b = 1;
let add1 = () => {
a++;
}
let add2 = () => {
a = b + 1;
}
`;
let ast = acorn.parse(a, { ecmaVersion: 2023 });
walk(ast, {
enter(node) {
console.log('ast node', node);
if (node.type === 'UpdateExpression' || node.type === 'AssignmentExpression') {
const names = extract_names(node.type === 'UpdateExpression' ? node.argument : node.left);
console.log('variable names', names)
}
},
leave(node) {}
})
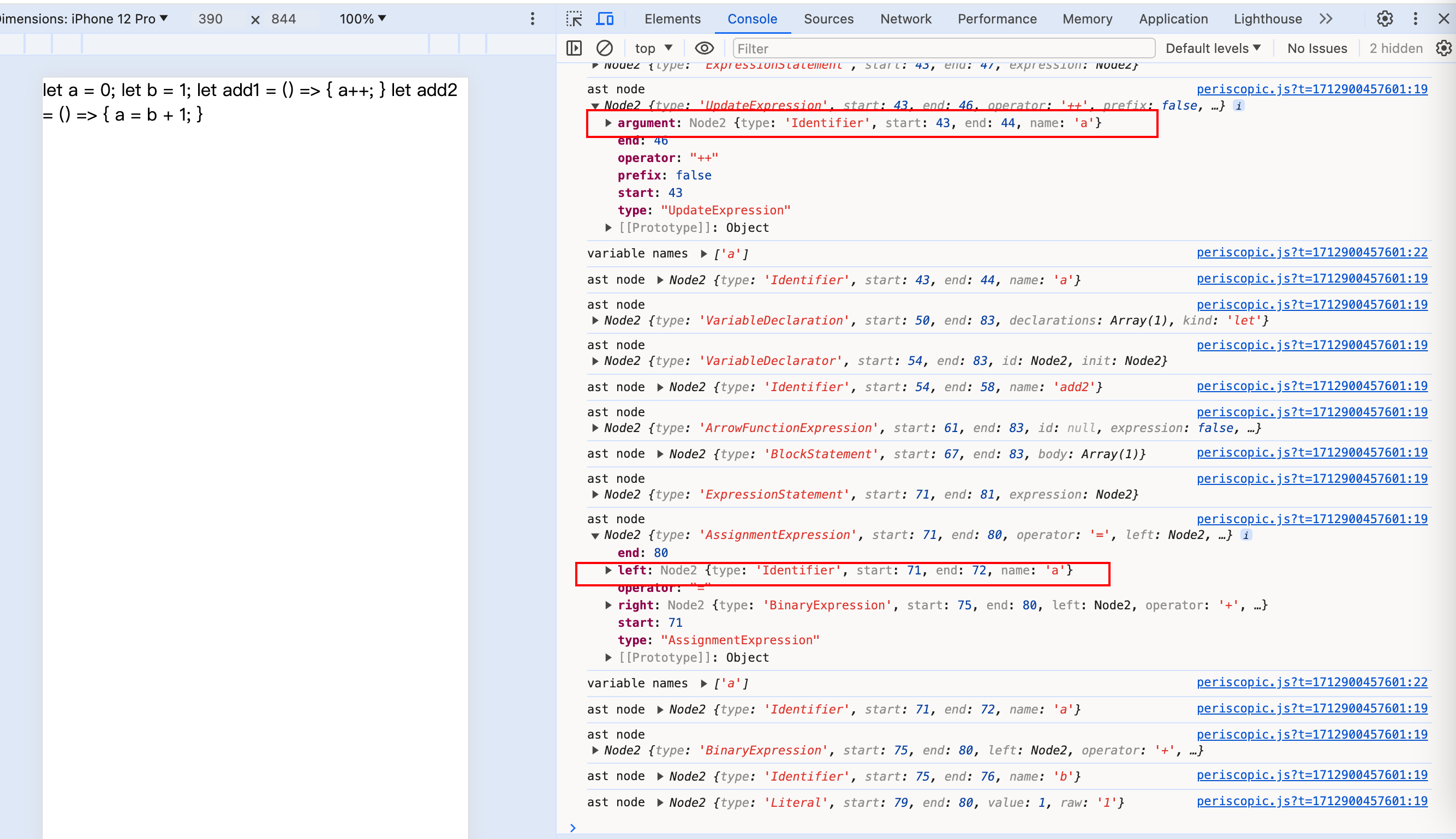
我们可以看到,UpdateExpression对应的是a++相关节点,通过extract_names取node.argument里的name即是自增赋值后要更新的变量a,而AssignmentExpression对应的是a = b + 1;,extract_names需要取node.left里的name,才能取到被赋值后的变量。
解析html
完善analyse方法:
function traverse(fragment) {
switch(fragment.type) {
case 'Element':
fragment.children.forEach((child) => traverse(child));
break;
case 'Expression': {
periscopic.extract_names(fragment.expression).forEach((name) => {
result.willUseInTemplate.add(name);
});
break;
}
}
}
ast.html.forEach(fragment => traverse(fragment));
willUseInTemplate用来存储在html模板语法内使用到的变量,比如以下例子:
<div>{count}</div>
{count}中的count会被记录到willUseInTemplate中。
编译
完善generate方法:
function generate(ast, analysis) {
const code = {
variables: [],
create: [],
+ update: [],
destroy: [],
};
...
}
添加update属性,用来存放更新逻辑的代码。
编译script
在generate方法中添加:
const { rootScope, map } = analysis;
let currentScope = rootScope;
estreewalker.walk(ast.script, {
enter(node, parent) {
if (map.has(node)) {
currentScope = map.get(node)
}
if (node.type === 'UpdateExpression' || node.type === 'AssignmentExpression') {
const names = periscopic
.extract_names(
node.type === 'UpdateExpression' ? node.argument : node.left
)
.filter(
(name) =>
currentScope.find_owner(name) === rootScope &&
analysis.willUseInTemplate.has(name)
);
if (names.length > 0) {
this.replace({
type: 'SequenceExpression',
expressions: [
node,
acorn.parseExpressionAt(`$$update(${JSON.stringify(names)})`, 0, {
ecmaVersion: 2023,
}),
],
});
this.skip();
}
}
},
leave(node) {
if (map.has(node)) {
currentScope = currentScope.parent;
}
}
});
- 一个比较重要的步骤是使用
periscopic的extract_names方法提取出所有的变量名,然后过滤出在根作用域中并且在模板中会使用的变量名。 - 如果我们筛选出了符合条件的变量名,我们在这个变量名后面添加一个约定字符串
$$update([x]),这个其实是一个方法,我们用它来模拟在运行时的$invalidate。
演示一个例子:
import * as acorn from "acorn";
import { walk } from "estree-walker";
import * as escodegen from "escodegen";
export let a = `() => { a = b + c}`;
let ast = acorn.parse(a, { ecmaVersion: 2023 });
walk(ast, {
enter(node) {
if (node.type === "BinaryExpression") {
this.replace({
type: "SequenceExpression",
expressions: [
node,
acorn.parseExpressionAt(`$$update()`, 0, {
ecmaVersion: 2023,
}),
],
});
this.skip();
}
},
});
let newCode = escodegen.generate(ast);
console.log('new code', newCode);
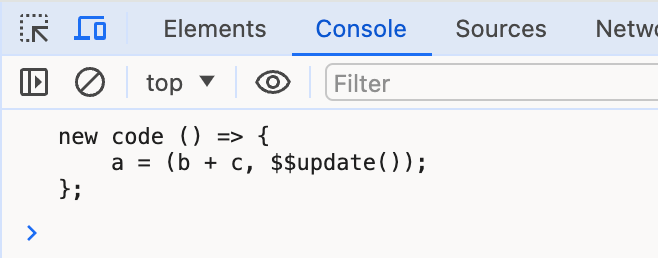
编译html
为Expression添加逻辑:
function generate(ast, analysis) {
const code = {
variables: [],
create: [],
update: [],
destroy: [],
};
let counter = 1;
function traverse(node, parent) {
switch (node.type) {
...
case "Expression": {
...
// 更新
const names = periscopic.extract_names(node.expression);
if (analysis.willChange.has(names[0])) {
let condition = `changed.includes('${names[0]}')`;
code.update.push(`if (${condition}) {
${variableName}.data = ${expressionStr};
}`);
}
break;
}
}
}
ast.html.forEach((fragment) => traverse(fragment, "target"));
...
}
- 首先我们从expression表达式中的变量中筛选出即将要更新的变量
- 这里我们假设我们的
{}表达式内只存在一个变量。willChange中记录的是被赋值后将要更新的变量,判断{}内获取到的变量名是否存在在willChange集合中,是的话填写我们的编译后的判断条件代码,把这部分执行逻辑放到code.update中,让它在变量更新后执行。
最后,我们需要完善我们默认导出的字符串模板内容
function generate(ast, analysis) {
return `
...
export default function() {
${code.variables.map((v) => `let ${v};`).join("\n")}
let collectChanges = [];
function $$update(changed) {
changed.forEach(c => collectChanges.push(c));
lifecycle.update(collectChanges);
}
${escodegen.generate(ast.script)}
var lifecycle = {
create(target) {
${code.create.join("\n")}
},
update(changed) {
${code.update.join('\n')}
},
destroy(target) {
${code.destroy.join("\n")}
}
};
return lifecycle;
}
`;
}
- 添加
$$update方法,这个方法我们在前面已经通过逻辑判断,只要变量会更新,在后面便会带上该方法。 lifecycle中补充update的逻辑,展开code.update中已经存放好的update生命周期的方法。
我们修改App.svelte的内容测试一下:
<script>
let count = 0;
const updateCount = () => {
count++;
console.log('update count', count);
}
</script>
<button on:click={updateCount}>add</button>
count: {count}
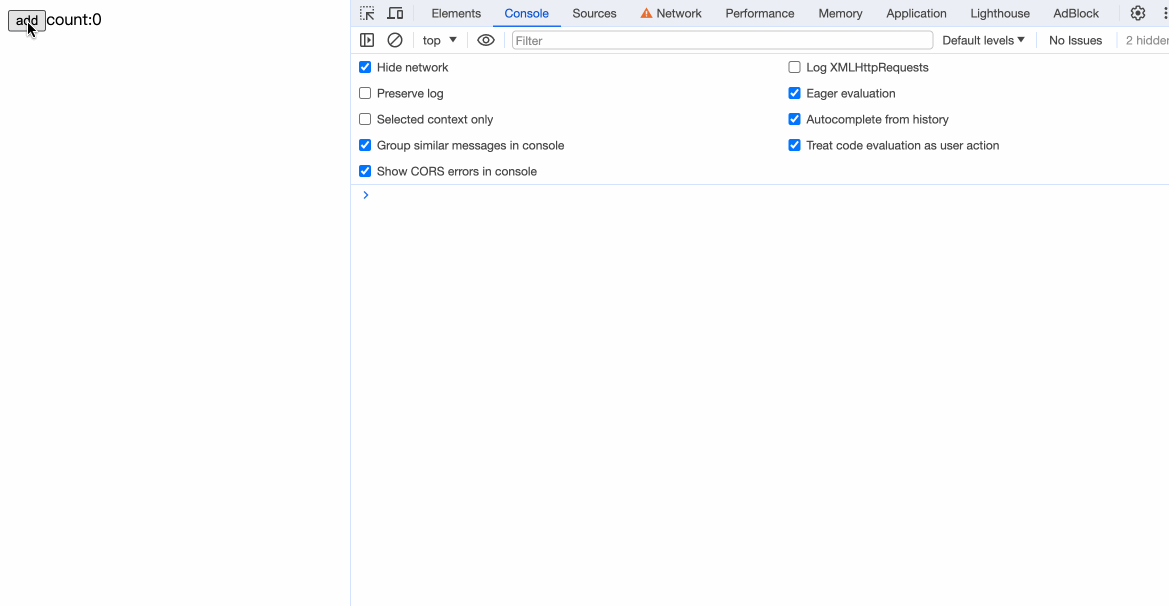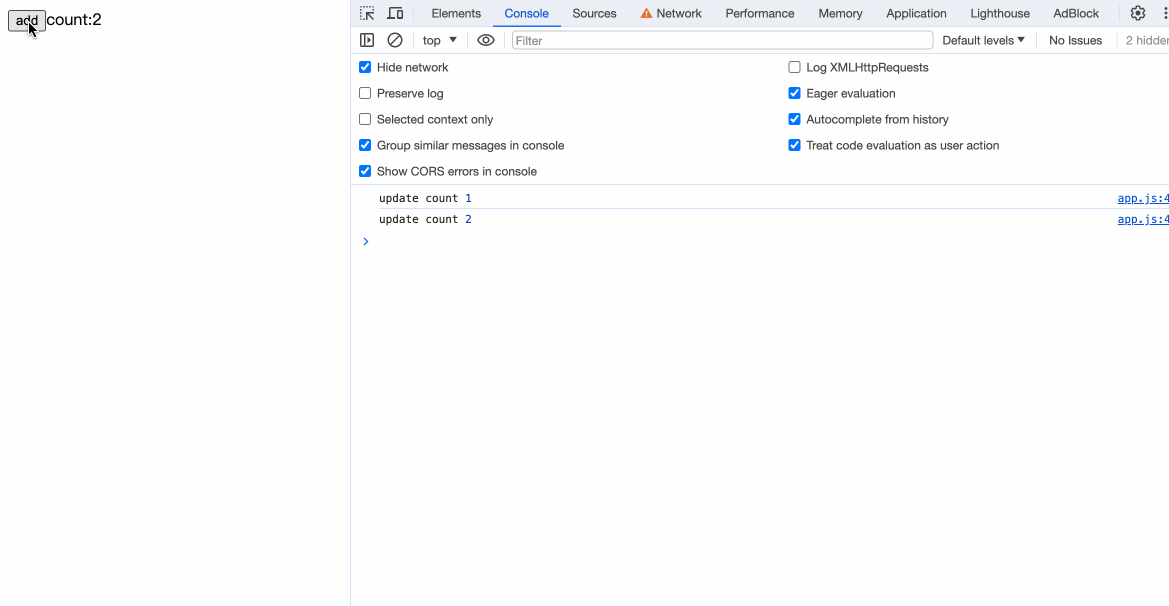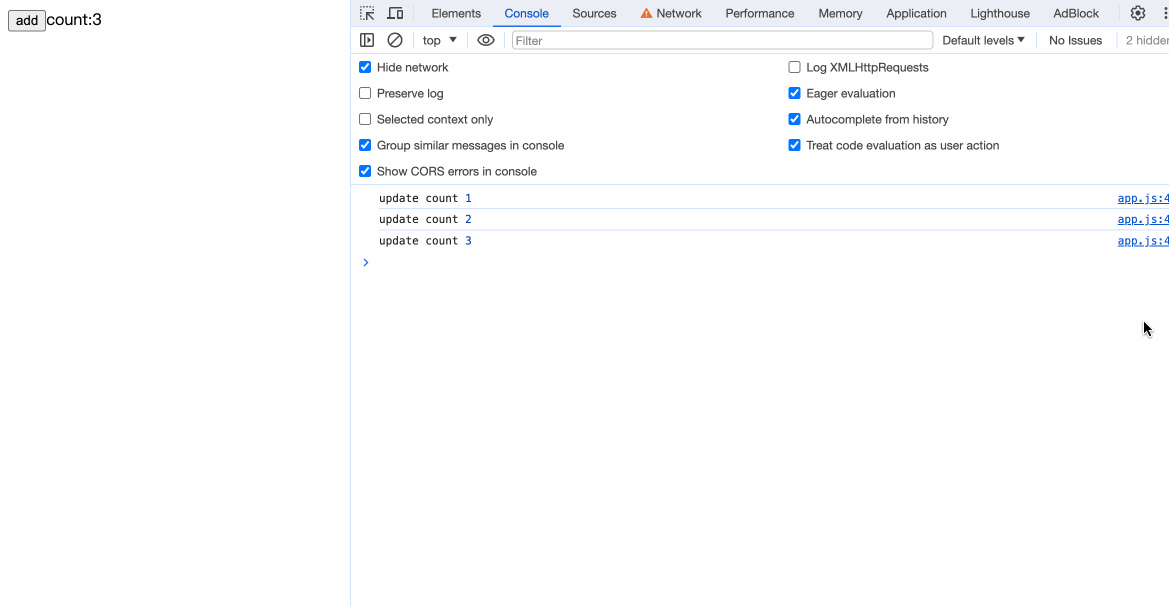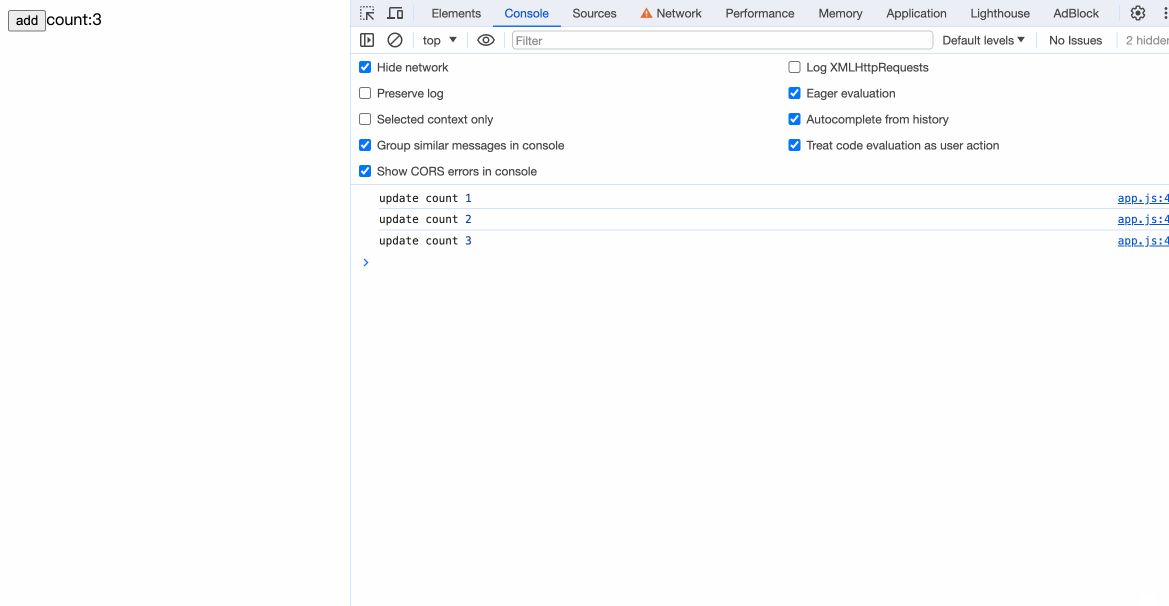
观察编译后的代码,发现在count++后携带了$$update([count]):
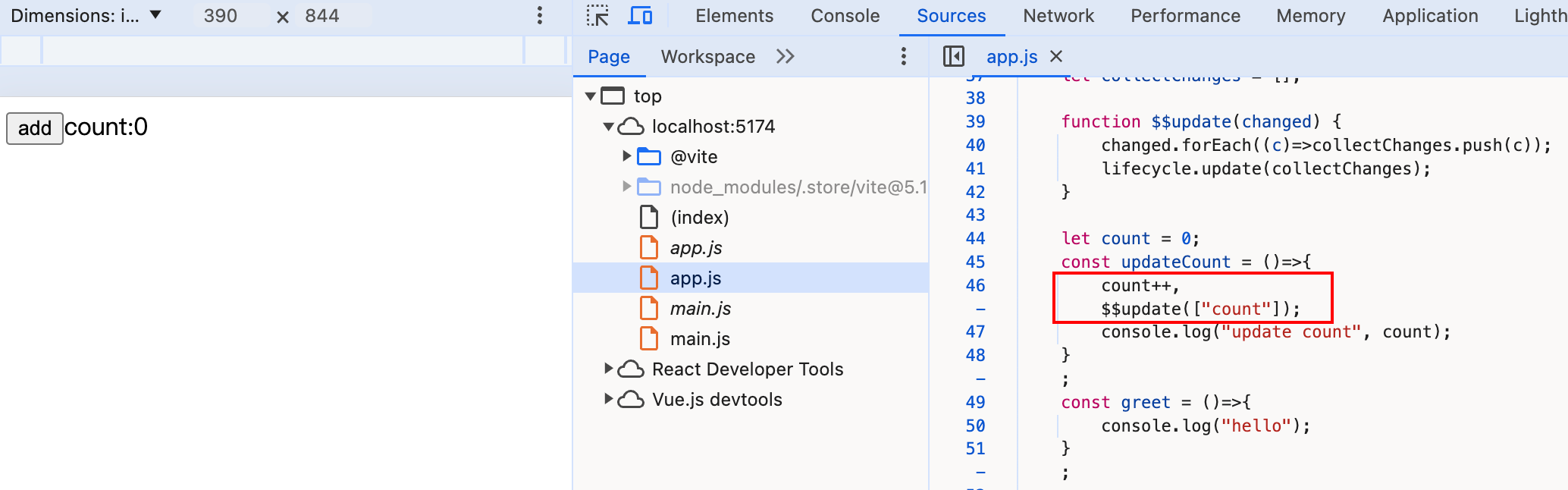
到这里,一个最最基本的Svelte编译器已经完成!
完整代码
import * as fs from "fs";
import { fileURLToPath } from "url";
import { dirname, resolve } from "path";
import * as acorn from "acorn";
import * as escodegen from "escodegen";
import * as prettier from "prettier";
import * as estreewalker from "estree-walker";
import * as periscopic from "periscopic";
const modulePath = dirname(fileURLToPath(import.meta.url));
async function bootstrap() {
try {
const inputPath = resolve(modulePath, "./App.svelte");
const outputPath = resolve(modulePath, "./app.js");
const content = fs.readFileSync(inputPath, "utf-8");
const compiledContent = compile(content);
const prettierContent = await prettier.format(compiledContent, {
parser: "babel",
});
fs.writeFileSync(outputPath, prettierContent, "utf-8");
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
}
function compile(content) {
const ast = parse(content); // 解析svelte文件内容成ast
const analysis = analyse(ast);
return generate(ast, analysis);
}
function parse(content) {
let i = 0;
const ast = {};
ast.html = parseFragments(() => i < content.length);
return ast;
function parseFragments(condition) {
const fragments = [];
while (condition()) {
const fragment = parseFragment();
if (fragment) {
fragments.push(fragment);
}
}
return fragments;
}
function parseFragment() {
return parseScript() ?? parseElement() ?? parseText() ?? parseExpression();
}
function parseScript() {
skipWhitespace();
if (match("<script>")) {
eat("<script>");
const startIndex = i;
const endIndex = content.indexOf("</script>", i);
const code = content.slice(startIndex, endIndex);
ast.script = acorn.parse(code, { ecmaVersion: 2023 });
i = endIndex;
eat("</script>");
skipWhitespace();
}
}
function parseElement() {
skipWhitespace();
if (match("<")) {
eat("<");
const tagName = readWhileMatching(/[a-z]/);
const attributes = parseAttributes();
eat(">");
const endTag = `</${tagName}>`;
const element = {
type: "Element",
name: tagName,
attributes,
children: parseFragments(() => !match(endTag)),
};
eat(endTag);
skipWhitespace();
return element;
}
}
function parseAttributes() {
skipWhitespace();
const attributes = [];
while (!match(">")) {
attributes.push(parseAttribute());
skipWhitespace();
}
return attributes;
}
function parseAttribute() {
const name = readWhileMatching(/[^=]/);
if (match("={")) {
eat("={");
const value = parseJavaScript();
eat("}");
return {
type: "Attribute",
name,
value,
};
}
}
function parseExpression() {
if (match("{")) {
eat("{");
const expression = parseJavaScript();
eat("}");
return {
type: "Expression",
expression,
};
}
}
function parseJavaScript() {
const js = acorn.parseExpressionAt(content, i, { ecmaVersion: 2023 });
i = js.end;
return js;
}
function parseText() {
const text = readWhileMatching(/[^<{]/);
if (text.trim() !== "") {
return {
type: "Text",
value: text.trim(),
};
}
}
function match(str) {
return content.slice(i, i + str.length) === str;
}
function eat(str) {
if (match(str)) {
i += str.length;
} else {
throw new Error(`Parse error: expecting "${str}"`);
}
}
function readWhileMatching(reg) {
let startIndex = i;
while (i < content.length && reg.test(content[i])) {
i++;
}
return content.slice(startIndex, i);
}
function skipWhitespace() {
readWhileMatching(/[\s\n]/);
}
}
function analyse(ast) {
const result = {
variables: new Set(),
willChange: new Set(),
useInTemplate: new Set(),
};
const { scope: rootScope, map, globals } = periscopic.analyze(ast.script);
result.variables = new Set(rootScope.declarations.keys());
result.rootScope = rootScope;
result.map = map;
let currentScope = rootScope;
estreewalker.walk(ast.script, {
enter(node) {
if (map.has(node)) {
currentScope = map.get(node);
}
if (
node.type === "UpdateExpression" ||
node.type === "AssignmentExpression"
) {
const names = periscopic.extract_names(
node.type === "UpdateExpression" ? node.argument : node.left
);
for (const name of names) {
if (
currentScope.find_owner(name) === rootScope ||
globals.has(name)
) {
result.willChange.add(name);
}
}
}
},
leave(node) {
if (map.has(node)) {
currentScope = currentScope.parent;
}
},
});
function traverse(fragment) {
switch (fragment.type) {
case "Element":
fragment.children.forEach((child) => traverse(child));
break;
case "Expression": {
periscopic.extract_names(fragment.expression).forEach((name) => {
result.useInTemplate.add(name);
});
break;
}
}
}
ast.html.forEach((fragment) => traverse(fragment));
return result;
}
function generate(ast, analysis) {
const code = {
variables: [],
create: [],
update: [],
destroy: [],
};
let counter = 1;
function traverse(node, parent) {
switch (node.type) {
case "Element": {
const variableName = `${node.name}_${counter++}`;
code.variables.push(variableName);
code.create.push(`${variableName} = element('${node.name}')`);
node.attributes.forEach((attribute) => {
traverse(attribute, variableName);
});
node.children.forEach((child) => {
traverse(child, variableName);
});
code.create.push(`append(${parent}, ${variableName})`);
code.destroy.push(`detach(${variableName})`);
break;
}
case "Text": {
const variableName = `txt_${counter++}`;
code.variables.push(variableName);
code.create.push(`${variableName} = text('${node.value}');`);
code.create.push(`append(${parent}, ${variableName})`);
code.destroy.push(`detach(${variableName})`);
break;
}
case "Attribute": {
if (node.name.startsWith("on:")) {
const eventName = node.name.slice(3);
const eventHandler = node.value.name;
const eventNameCall = `${eventName}_${counter++}`;
code.variables.push(eventNameCall);
code.create.push(
`${eventNameCall} = listen(${parent}, "${eventName}", ${eventHandler})`
);
code.destroy.push(`${eventNameCall}()`);
}
break;
}
case "Expression": {
const variableName = `exp_${counter++}`;
const expressionStr = escodegen.generate(node.expression);
code.variables.push(variableName);
code.create.push(`${variableName} = text(${expressionStr})`);
code.create.push(`append(${parent}, ${variableName});`);
// 更新
const names = periscopic.extract_names(node.expression);
if (analysis.willChange.has(names[0])) {
let condition = `changed.includes('${names[0]}')`;
code.update.push(`if (${condition}) {
${variableName}.data = ${expressionStr};
}`);
}
break;
}
}
}
ast.html.forEach((fragment) => traverse(fragment, "target"));
const { rootScope, map } = analysis;
let currentScope = rootScope;
estreewalker.walk(ast.script, {
enter(node, parent) {
if (map.has(node)) {
currentScope = map.get(node)
}
if (node.type === 'UpdateExpression' || node.type === 'AssignmentExpression') {
const names = periscopic
.extract_names(
node.type === 'UpdateExpression' ? node.argument : node.left
)
.filter(
(name) =>
currentScope.find_owner(name) === rootScope &&
analysis.useInTemplate.has(name)
);
if (names.length > 0) {
this.replace({
type: 'SequenceExpression',
expressions: [
node,
acorn.parseExpressionAt(`$$update(${JSON.stringify(names)})`, 0, {
ecmaVersion: 2023,
}),
],
});
this.skip();
}
}
},
leave(node) {
if (map.has(node)) {
currentScope = currentScope.parent;
}
}
});
return `
function element(name) {
return document.createElement(name);
}
function text(data) {
return document.createTextNode(data);
}
function append(target, node) {
target.appendChild(node);
}
function detach(node) {
if (node.parentNode) {
node.parentNode.removeChild(node);
}
}
export function listen(node, event, handler) {
node.addEventListener(event, handler);
return () => node.removeEventListener(event, handler);
}
export default function() {
${code.variables.map((v) => `let ${v};`).join("\n")}
let collectChanges = [];
function $$update(changed) {
changed.forEach(c => collectChanges.push(c));
lifecycle.update(collectChanges);
}
${escodegen.generate(ast.script)}
var lifecycle = {
create(target) {
${code.create.join("\n")}
},
update(changed) {
${code.update.join('\n')}
},
destroy(target) {
${code.destroy.join("\n")}
}
};
return lifecycle;
}
`;
}
bootstrap();
小结
本章我们实现了:
- 解析html模板内的变量
- 收集文件中存在更新操作的变量
- 对
<script></script>标签内的更新方法进行重新编译,编译成能够触发框架更新的$$update方法
